 |
 |
| English name | Hunting dogs | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Major stars | alpha Canum Venaticorum | Cor Caroli | magn. 2,9 | RA: 12h 56m 01.71s | Dec: +38° 19' 06.1" |
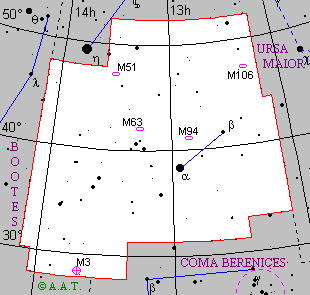
| Description | Small constellation, situated between Bootes and Ursa Maior. Its principal star, alpha Canum Venaticorum, was denominated Cor Caroli ("Charles' heart", in Latin) by Sir Charles Scarborough, in honor of king Charles I of England.
On the border with the constellation of Bootes, in the southern zone of the constellation, there is M3 a globular cluster that at binoculars appears as an out-of-focus light ball. |
||||
| Mythology and history | The constellation was drawn in 1687 by Johannes Hevelius, using stars that in precedence belonged to the Ursa Maior. Canes Venatici represent two dogs that Bootes keeps on a lead: they stretch out to snap the Ursa Maior's legs. The more southern dog is marked by the two brightest stars, alpha and beta Canum Venaticorum; the more northern one by a small group of little bright stars. |
||||
 Back to constellations page.
Back to constellations page.